
- “In Europe, ESA has the unique ability to implement, together with industry, complex and ambitious space missions and programmes on an equal footing with other leading space agencies worldwide. We will ensure that this ESA strength and value is further reinforced.”
- "ESA will therefore digitalise its full project management, enabling the development of digital twins, both for engineering by using Model Based System Engineering, and for procurement and finance, achieving full digital continuity with industry.”
Motivation
As presented in the ESA Agenda 2025:
To increase the competitiveness of European ecosystems, it is of vital importance to spur the digitalisation of processes in the spacecraft development and operations.
Digitalisation is the process of transforming the artefacts of space systems into a (structured) digital representation on which computers can elaborate. The most explicit example of such digitalisation process is the Model Based technique, where the data and information (e.g. requirements, design, analysis, V&V) from different disciplines, traditionally captured and exchanged in the form of documents, is instead expressed in a set of data structured into a model. Computers can be programmed to navigate and search into the models, and create relations between associated data, allowing to discover more properties, and to derive added value such as traceability, optimisation, technical budgets, trends, and knowledge.
Digitalisation includes also e.g. databases or spreadsheets, or any format where data is structured, curated and associated to semantic layers (models) that allow to unambiguously understand it with a computer.
This transformation relies on common standards and new infrastructures that facilitate the exchange of data but also the collaboration along the whole supply chain.
The Digital Spacecraft is a new concept, derived from similar initiatives in other domains such as automotive or aviation, and introduced in ESA to cover the digital transformation of space, ground, launcher segments development and operation in all application domains, as a new way to collaborate within the space ecosystem throughout the full project lifecycle. It is based on a high degree of digitalisation and provides an umbrella to a wide spectrum of topics like MBSE, digital transformation. digital twins and full data integration into a single consistent concept covering all aspects related to a spacecraft.
An effective and efficient collaboration between industry and the Agencies, with continuous and active interaction to improve each model with a positive impact spacecraft development, is essential to facilitate the implementation of the Digital Spacecraft business/use cases and to allow responding to the identified user needs.
This is achieved by a number of working groups between Agencies and Industry, addressing specific aspects of the digitalisation. Each of them gives its own impulse to ESA digitalisation, similar to the stages of a rocket...
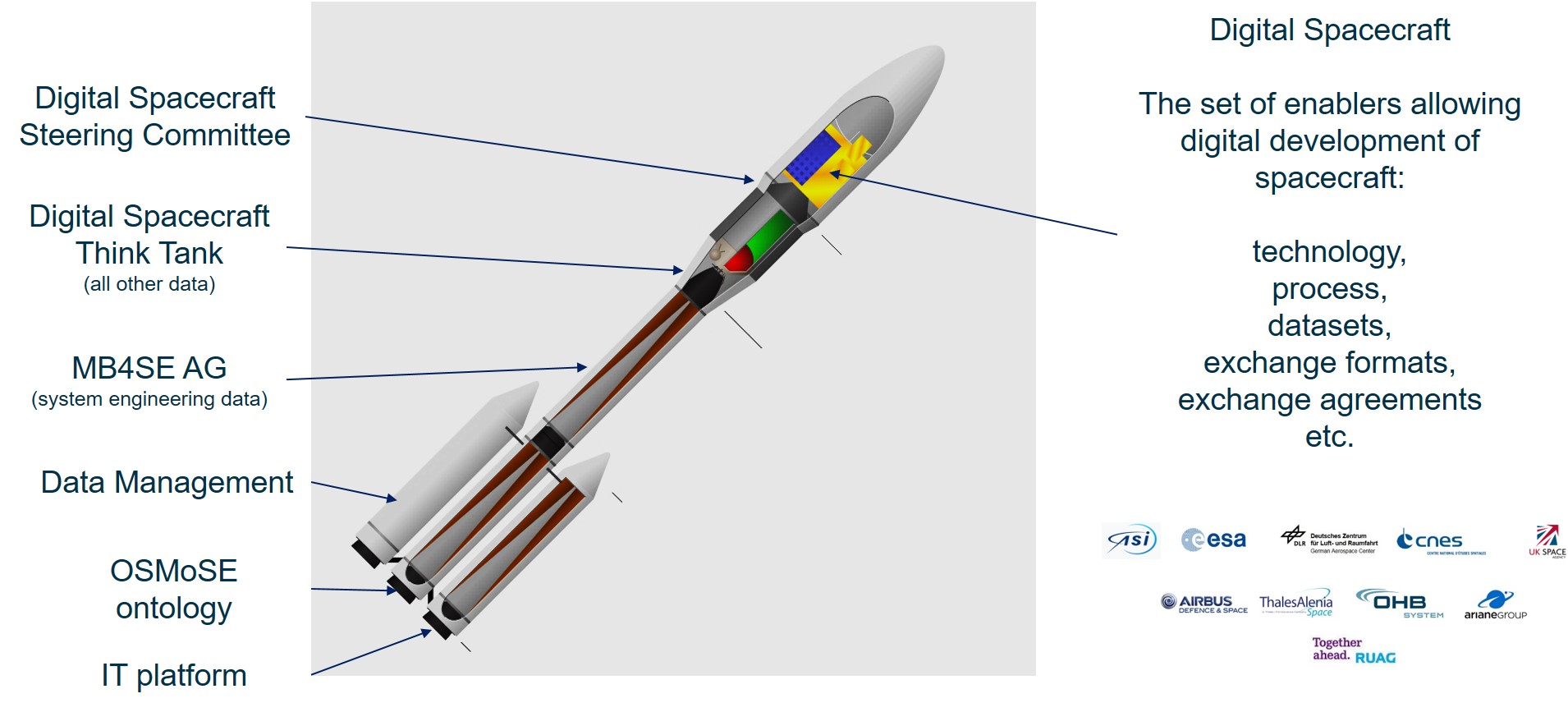
- The MB4SE Advisory Group (Model Based for System Engineering), addressing digitalisation of system engineering data,
- The Digital Spacecraft Think Tank (DtSC), addressing the digitalisation of the other data,
- The OSMoSE group (Overall Semantic Modelling for System Engineering), which defines the Space System Ontology to achieve the semantic operability between the data,
- The Data Management group, which defines which data are going to be used how, for which purpose, under which process, and therefore with which informatics needs,
- The IT Platform group, which analyses the informatic architecture needed to accomodate all the tools supporting the Digitalisation (for example, [extended] Entreprise concept).
- The Digital Spacecraft Steering Committee of managers empower the teams and endorse the common decisions.
Two of these groups are central to the initiative:
These two groups are boosted by:
The last group supervises the others:
The purpose of these groups is to deliver the "Digital Spacecraft", i.e. the set of enablers allowing the digital development of spacecraft (technology, process, datasets, exchange formats, exchange agreements, etc.).
Some links related to ESA digitalisation: